Understanding the basics of geometry is crucial for anyone looking to solve everyday problems or excel in mathematics. One of the most fundamental concepts in geometry is learning how to figure the circumference of a circle. Whether you're measuring the distance around a wheel, designing a circular garden, or calculating the dimensions of a circular object, knowing how to calculate the circumference is a valuable skill. This article dives deep into the topic, providing step-by-step guidance, practical examples, and expert tips to help you master this essential mathematical concept. By the end, you’ll not only know how to figure the circumference of a circle but also appreciate its real-world applications.
Many people find geometry intimidating, but with the right approach, it becomes much simpler. The circumference of a circle is essentially the distance around its edge, and calculating it involves a straightforward formula. However, understanding the logic behind the formula and knowing how to apply it in different scenarios is what sets apart those who merely memorize from those who truly grasp the concept. This article is designed to bridge that gap by breaking down the process into digestible steps and offering practical advice.
Whether you're a student preparing for an exam, a professional needing precise measurements, or simply someone curious about mathematics, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and confidence to tackle any problem involving the circumference of a circle. So, let’s dive in and explore the fascinating world of circles and their measurements!
Read also:How To Set Up Youtube Channel A Comprehensive Guide For Beginners
Table of Contents
- 1. Introduction to Circles and Their Measurements
- 2. What Is the Formula for Figuring the Circumference of a Circle?
- 3. Step-by-Step Guide: How to Figure the Circumference of a Circle
- 4. Real-World Applications of Circumference Calculations
- 5. Why Is It Important to Know How to Figure the Circumference of a Circle?
- 6. Common Errors to Avoid When Calculating Circumference
- 7. How Can Tricks and Shortcuts Help in Figuring the Circumference of a Circle?
- 8. Frequently Asked Questions
- 9. Conclusion
Introduction to Circles and Their Measurements
A circle is one of the simplest yet most fascinating shapes in geometry. Defined as a closed curve where all points are equidistant from the center, circles are found everywhere in nature and human-made structures. From the wheels of vehicles to the orbits of planets, circles play a vital role in our daily lives. To truly understand a circle, it’s essential to know how to measure its properties, such as the radius, diameter, and circumference.
The circumference of a circle is the linear distance around its edge. It’s a critical measurement used in various fields, including engineering, architecture, and physics. Unlike polygons, circles don’t have straight edges, making their measurement unique and requiring specific formulas. By learning how to figure the circumference of a circle, you gain the ability to solve a wide range of problems, from designing circular objects to calculating distances.
In this section, we’ll explore the basic terminology associated with circles, such as radius, diameter, and pi (π). These terms are the building blocks of understanding how to calculate the circumference. As we delve deeper, you’ll see how these concepts interconnect and form the foundation of this essential mathematical skill.
What Is the Formula for Figuring the Circumference of a Circle?
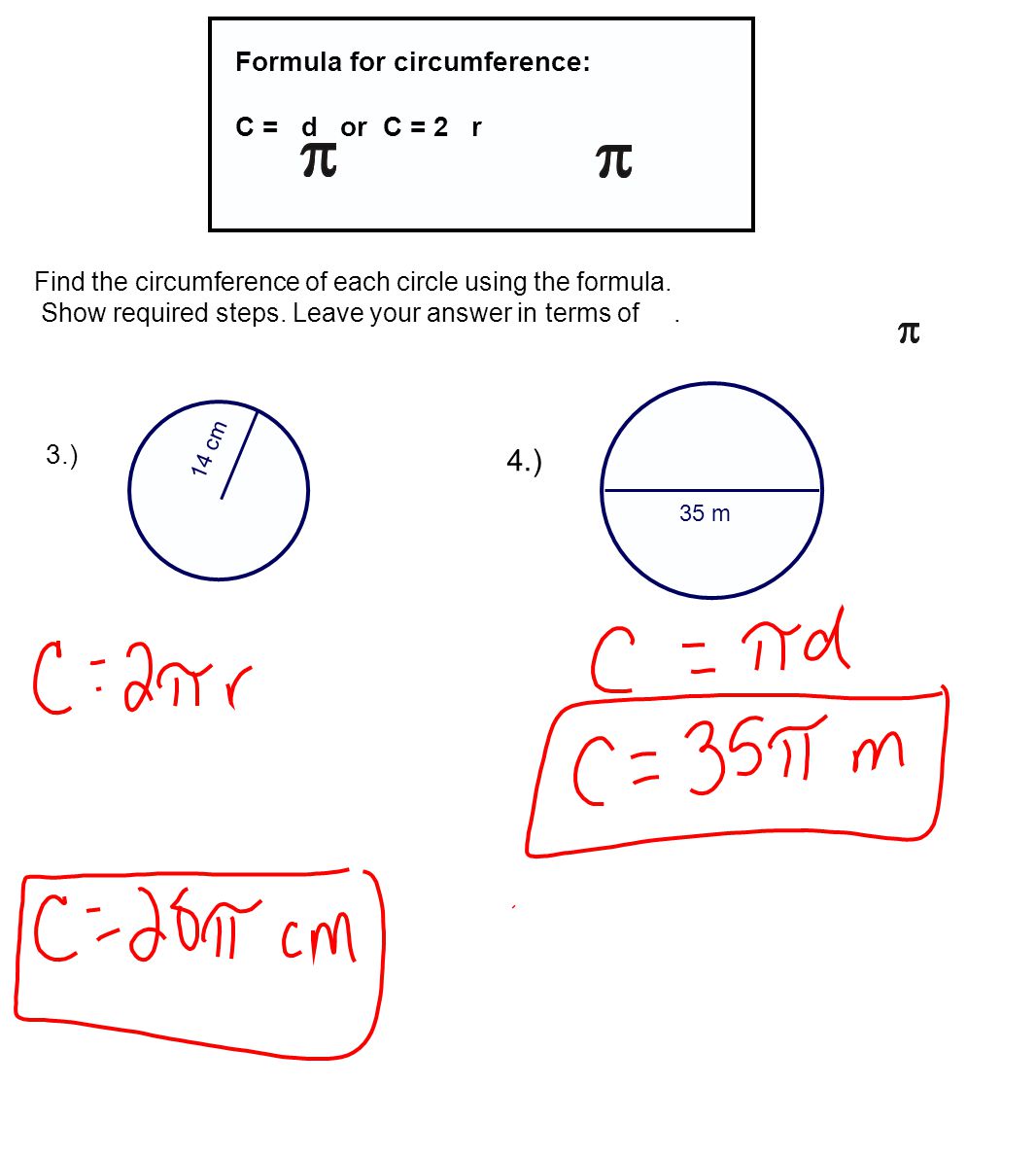
At the heart of calculating the circumference of a circle lies a simple yet powerful formula: \( C = 2 \pi r \). Here, \( C \) represents the circumference, \( r \) is the radius of the circle, and \( \pi \) (pi) is a mathematical constant approximately equal to 3.14159. This formula is derived from the relationship between the diameter and the circumference of a circle, which is always proportional to \( \pi \).
Another variation of the formula uses the diameter (\( d \)) instead of the radius: \( C = \pi d \). Since the diameter is twice the radius (\( d = 2r \)), both formulas yield the same result. Understanding these variations allows you to choose the most convenient formula depending on the information provided in a problem.
It’s important to note that \( \pi \) is an irrational number, meaning it cannot be expressed as an exact fraction or decimal. However, for practical purposes, approximations like 3.14 or 22/7 are often used. This flexibility makes the formula adaptable to different levels of precision required by various applications.
Read also:The Ultimate Guide To Tiempo Para Los Angeles Weather Patterns And Lifestyle Insights
Why Is Pi So Important in Calculating Circumference?
Pi (\( \pi \)) is not just a random number but a fundamental constant in mathematics. It represents the ratio of a circle’s circumference to its diameter, a relationship that holds true for all circles regardless of their size. This universality is what makes \( \pi \) so significant in geometry and beyond. By incorporating \( \pi \) into the formula, we ensure that our calculations are accurate and consistent.
Furthermore, \( \pi \) appears in numerous other mathematical and scientific contexts, from trigonometry to quantum mechanics. Its importance extends far beyond the realm of circles, making it a cornerstone of modern mathematics. Understanding its role in calculating the circumference is just the beginning of appreciating its broader significance.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Figure the Circumference of a Circle
Now that we’ve covered the basics, let’s walk through the process of calculating the circumference step by step. This method ensures clarity and accuracy, even for beginners. Follow these simple instructions, and you’ll be able to solve any problem involving the circumference of a circle with confidence.
- Identify the Given Information: Determine whether you’re provided with the radius (\( r \)) or the diameter (\( d \)) of the circle. If neither is given, you may need to measure the circle directly or use additional information to find one of these values.
- Select the Appropriate Formula: Choose between \( C = 2 \pi r \) and \( C = \pi d \), depending on which measurement you have. If you’re given the radius, use the first formula; if you’re given the diameter, use the second.
- Substitute the Values: Replace \( r \) or \( d \) in the formula with the corresponding numerical value from the problem. Be sure to use the correct units of measurement.
- Perform the Calculation: Multiply the values as indicated in the formula. For example, if the radius is 5 cm, the calculation would be \( C = 2 \times 3.14 \times 5 = 31.4 \) cm.
- Double-Check Your Work: Verify your calculations to ensure accuracy. Mistakes in arithmetic or unit conversion can lead to incorrect results.
By following these steps, you can systematically figure the circumference of a circle, regardless of the complexity of the problem. Practice is key to mastering this skill, so try solving a variety of examples to reinforce your understanding.
Real-World Applications of Circumference Calculations
The ability to figure the circumference of a circle has numerous practical applications across different industries. From construction to sports, this skill is indispensable in solving real-world problems. Let’s explore some of the most common scenarios where circumference calculations come into play.
In construction, architects and engineers use circumference formulas to design circular structures such as domes, roundabouts, and water tanks. Accurate measurements ensure that these structures are both functional and aesthetically pleasing. Similarly, in manufacturing, the circumference of wheels and gears is critical for ensuring proper alignment and performance.
Sports enthusiasts also rely on circumference calculations. For instance, track and field events require precise measurements of running tracks and throwing circles. Even in everyday activities like crafting or gardening, knowing how to figure the circumference of a circle can help you plan and execute projects more effectively.
How Can Circumference Calculations Benefit Everyday Life?
Beyond professional applications, understanding how to figure the circumference of a circle can enhance your daily life. For example, when purchasing a circular rug or tablecloth, knowing the circumference helps you choose the right size. Similarly, if you’re planning a circular garden or flower bed, calculating the circumference ensures efficient use of space and resources.
In addition, this knowledge fosters a deeper appreciation for the mathematics underlying the world around us. Whether you’re admiring the symmetry of a circular building or marveling at the precision of a mechanical component, understanding circumference adds a layer of insight to your observations.
Why Is It Important to Know How to Figure the Circumference of a Circle?
Knowing how to figure the circumference of a circle is more than just a mathematical skill; it’s a gateway to understanding the world. Circles are ubiquitous in nature and human design, and their properties govern countless phenomena. By mastering this concept, you gain the ability to analyze and solve problems in a variety of contexts.
From a practical standpoint, circumference calculations are essential in fields like engineering, physics, and architecture. Professionals in these areas rely on precise measurements to design and build structures, machines, and systems that function efficiently and safely. Moreover, the ability to calculate circumference demonstrates a solid foundation in geometry, a key component of mathematical literacy.
On a personal level, understanding how to figure the circumference of a circle enhances your problem-solving skills and boosts your confidence in mathematics. It empowers you to approach challenges with a logical mindset and a toolbox of proven techniques. Whether you’re solving a complex equation or measuring a circular object, this knowledge provides a reliable framework for success.
Common Errors to Avoid When Calculating Circumference
Even with a clear understanding of the formula, mistakes can occur when calculating the circumference of a circle. Being aware of these common pitfalls can help you avoid them and ensure accurate results. Below are some of the most frequent errors and tips for preventing them.
- Confusing Radius and Diameter: Always double-check which measurement you’re using. Mixing up the radius and diameter can lead to incorrect calculations. Remember, the diameter is twice the radius (\( d = 2r \)).
- Using the Wrong Value for Pi: While approximations like 3.14 or 22/7 are acceptable in most cases, using an imprecise value for \( \pi \) can affect the accuracy of your results. Choose the level of precision appropriate for the problem at hand.
- Forgetting Units of Measurement: Units are crucial in mathematical calculations. Always include them in your final answer and ensure they match the units of the given measurements.
- Making Arithmetic Mistakes: Even a small error in multiplication or division can throw off your entire calculation. Take your time and verify each step to minimize mistakes.
By staying vigilant and following best practices, you can minimize errors and improve the reliability of your circumference calculations. Practice and experience will further refine your skills, making you more adept at solving these types of problems.
How Can Tricks and Shortcuts Help in Figuring the Circumference of a Circle?
While the standard formulas for calculating circumference are straightforward, there are tricks and shortcuts that can simplify the process, especially for mental calculations or quick estimations. These techniques leverage patterns and approximations to make the math easier without sacrificing accuracy.
One such trick involves using the relationship between the radius and the circumference. Since \( C \approx 6r \) (using \( \pi \approx 3 \)), you can quickly estimate the circumference by multiplying the radius by 6. This method is particularly useful for rough calculations or when exact precision isn’t required.
Another shortcut is to memorize common values of \( \pi \) multiplied by small integers. For example, knowing that \( \pi \times 1 = 3.14 \), \( \pi \times 2 = 6.28 \), and so on, can speed up your calculations significantly. Combining these shortcuts with practice can make figuring the circumference of a circle second nature.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Happens If I Don’t Know the Radius or Diameter?
If neither the radius nor the diameter is provided, you’ll need to measure the circle directly. Use a flexible measuring tape or a string to trace the circle’s edge, then measure the length of the string. This length represents the circumference. Alternatively, if you can measure the circle’s diameter or radius indirectly, you can use the appropriate formula to calculate the circumference.
Can I Use Different Units for Radius and Circumference?
Yes, but it’s essential to convert all measurements to the same unit before performing calculations. Mixing units can lead