When it comes to understanding the nuances of pregnancy-related health markers, urobilinogen 4.0 in urine pregnancy is a topic that deserves close attention. This specific measurement in urine can provide critical insights into liver function, metabolism, and overall health during pregnancy. For expectant mothers, recognizing the significance of urobilinogen levels is essential to maintaining a healthy pregnancy journey. Urobilinogen is a natural compound produced during the breakdown of red blood cells, and its presence in urine can signal various physiological changes. While urobilinogen levels vary from person to person, a reading of 4.0 during pregnancy might indicate underlying health conditions or normal physiological adaptations. Understanding what this means and how to address it is crucial for both healthcare providers and pregnant women.
Pregnancy brings about numerous changes in the body, and monitoring these changes through routine tests can help ensure the well-being of both mother and baby. Urobilinogen testing is one such diagnostic tool that provides valuable information about liver health and metabolic processes. In some cases, elevated urobilinogen levels in urine may point to liver dysfunction or other conditions that require medical attention. However, during pregnancy, certain physiological adaptations can also influence these levels. This article aims to demystify urobilinogen 4.0 in urine pregnancy, offering a detailed exploration of its implications, potential causes, and strategies for managing it effectively. Whether you're a healthcare professional or a concerned parent-to-be, this guide will equip you with the knowledge you need.
Before diving into the specifics, it's important to note that urobilinogen testing is just one piece of the larger puzzle when it comes to pregnancy health monitoring. While a reading of 4.0 might raise concerns, it's always best to consult with a healthcare provider who can interpret the results in the context of your overall health. This article will explore the role of urobilinogen in pregnancy, potential causes of elevated levels, and practical steps to address them. By the end, you'll have a clearer understanding of what urobilinogen 4.0 in urine pregnancy means and how it can be managed to support a healthy pregnancy journey.
Read also:Explore The Ultimate Playlist Best Songs About Love On Youtube In 2023
What Is Urobilinogen and Why Does It Matter During Pregnancy?
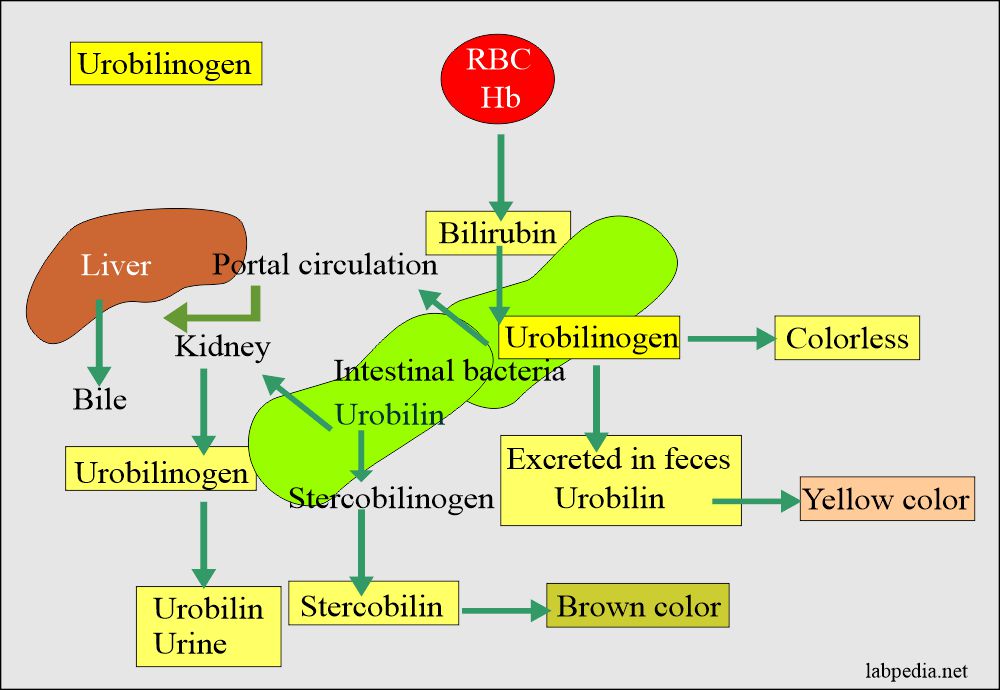
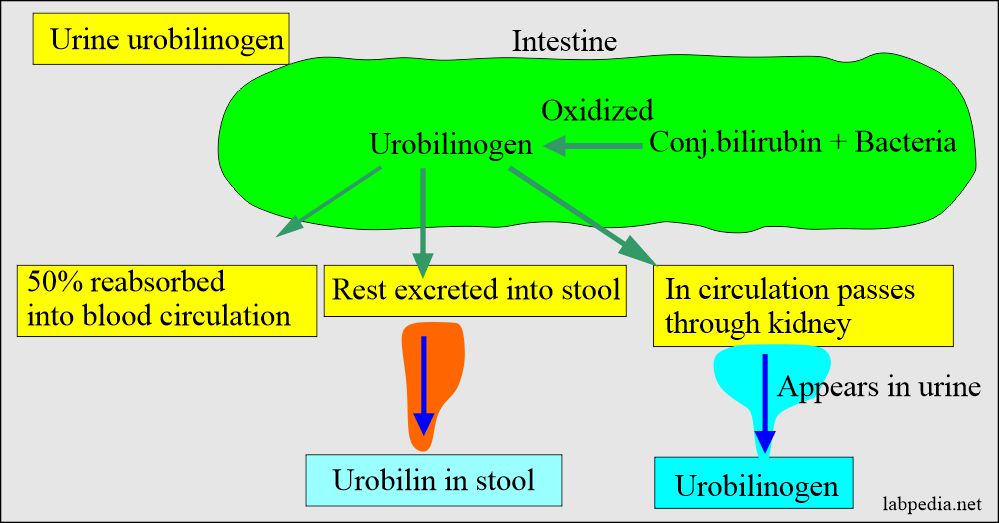
Urobilinogen is a compound produced during the breakdown of hemoglobin in red blood cells. It plays a critical role in the body's metabolic processes, particularly in the liver and digestive system. During pregnancy, the body undergoes significant changes, and urobilinogen levels can fluctuate due to these adaptations. Understanding the basics of urobilinogen is essential for interpreting test results and addressing any potential health concerns.
For pregnant women, urobilinogen levels in urine can provide insights into liver function, bile production, and overall metabolic health. Elevated levels, such as urobilinogen 4.0 in urine pregnancy, may indicate liver dysfunction, hemolytic anemia, or other underlying conditions. However, it's important to consider the context of pregnancy, as hormonal changes and increased metabolic demands can influence these readings. Regular monitoring and consultation with healthcare providers are crucial for accurate interpretation and appropriate management.
Here are some key points to consider:
- Urobilinogen is a byproduct of hemoglobin breakdown.
- It plays a role in bile production and excretion.
- Elevated levels during pregnancy may have physiological or pathological causes.
In summary, urobilinogen testing is a valuable tool for assessing health during pregnancy, but its interpretation must be done with care and consideration of the broader context.
How Does Urobilinogen Affect Liver Function During Pregnancy?
The liver undergoes significant changes during pregnancy to support the growing fetus and meet increased metabolic demands. Urobilinogen, as a marker of liver function, can provide insights into how well the liver is adapting to these changes. During pregnancy, the liver works harder to process hormones, nutrients, and waste products, which can influence urobilinogen levels in urine.
Elevated urobilinogen readings, such as urobilinogen 4.0 in urine pregnancy, may indicate increased bilirubin production or impaired bile excretion. This could be due to physiological adaptations, such as increased red blood cell turnover, or pathological conditions like liver disease. Pregnant women with pre-existing liver conditions or those experiencing symptoms like jaundice, fatigue, or abdominal pain should seek medical evaluation promptly.
Read also:How To Elevate Your Space With A Stunning 16 By 24 Inch Picture Frame
Healthcare providers often use urobilinogen testing in conjunction with other liver function tests to assess overall liver health. By monitoring these levels closely, they can identify potential issues early and implement appropriate interventions. For example, dietary adjustments, supplementation, or medication may be recommended to support liver function during pregnancy.
Why Is Urobilinogen Testing Important for Pregnant Women?
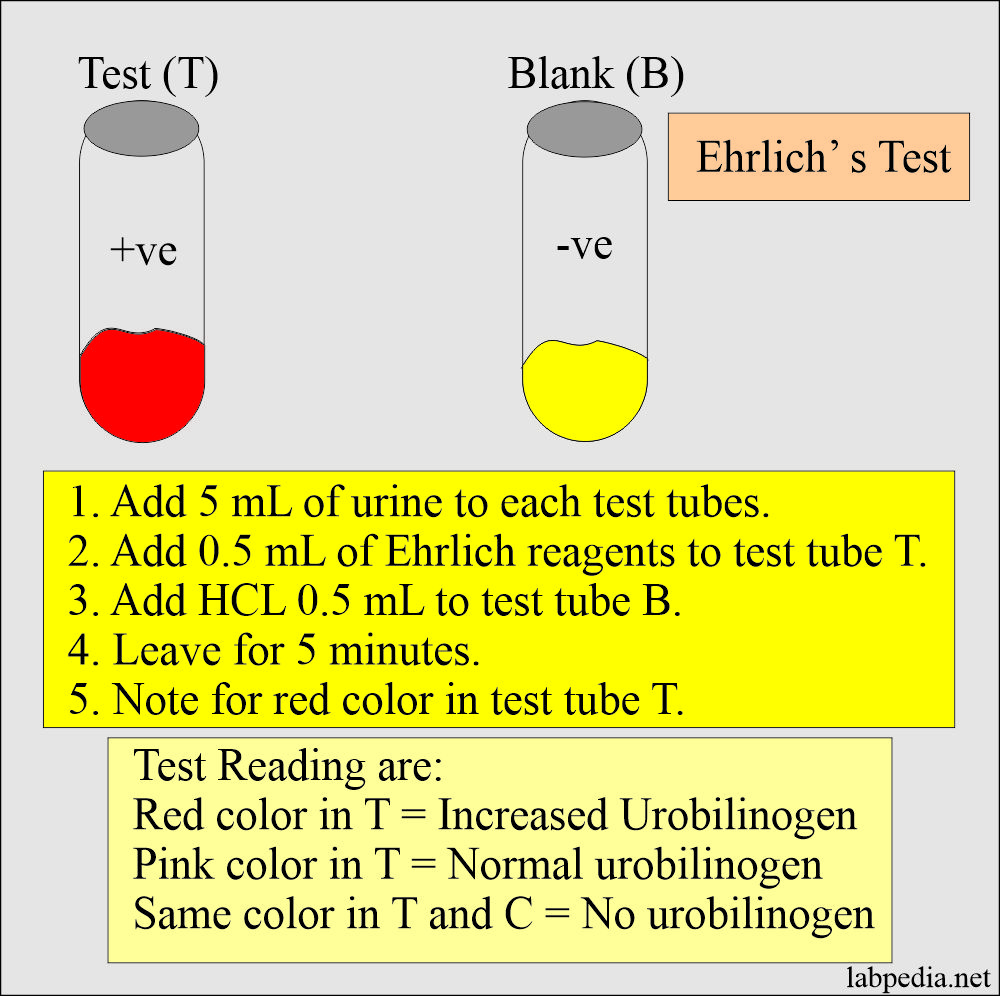
Urobilinogen testing is a non-invasive and cost-effective way to monitor liver function and metabolic health during pregnancy. It provides valuable information about the body's ability to process and excrete waste products, which is particularly important during this critical period. Elevated urobilinogen levels, such as urobilinogen 4.0 in urine pregnancy, can signal underlying health issues that require attention.
For expectant mothers, understanding the significance of urobilinogen testing can empower them to take proactive steps in managing their health. Regular testing allows for early detection of potential issues, enabling timely interventions and better outcomes. Healthcare providers can use these results to tailor care plans, ensuring that both mother and baby receive the support they need.
What Causes Elevated Urobilinogen Levels During Pregnancy?
Elevated urobilinogen levels during pregnancy can arise from a variety of physiological and pathological factors. While some causes are benign and related to normal pregnancy adaptations, others may indicate underlying health conditions that require medical attention. Understanding the potential causes of elevated urobilinogen, such as urobilinogen 4.0 in urine pregnancy, is essential for accurate diagnosis and appropriate management.
During pregnancy, the body experiences increased red blood cell turnover, which can lead to higher levels of bilirubin and, consequently, urobilinogen. This is a normal physiological adaptation that supports the growing fetus. However, other factors, such as liver disease, hemolytic anemia, or infections, can also contribute to elevated urobilinogen levels. Pregnant women with pre-existing conditions or those experiencing symptoms like jaundice, fatigue, or abdominal pain should seek medical evaluation.
Here are some potential causes of elevated urobilinogen levels during pregnancy:
- Increased red blood cell turnover
- Liver dysfunction or disease
- Hemolytic anemia
- Infections or inflammatory conditions
By identifying the underlying cause, healthcare providers can develop targeted treatment plans to address the issue effectively.
Is Urobilinogen 4.0 in Urine Pregnancy Normal?
The question of whether urobilinogen 4.0 in urine pregnancy is normal depends on various factors, including the individual's overall health, pregnancy stage, and other test results. While urobilinogen levels can fluctuate during pregnancy due to physiological adaptations, a reading of 4.0 may raise concerns in some cases. It's important to interpret this result in the context of the broader clinical picture.
In some instances, urobilinogen 4.0 in urine pregnancy may be within the normal range for that individual, particularly if they have a higher baseline level or are experiencing normal pregnancy-related changes. However, in other cases, it could indicate an underlying issue that requires further investigation. Healthcare providers often use additional tests, such as liver function tests, bilirubin levels, and imaging studies, to determine the cause and significance of elevated urobilinogen.
Pregnant women with urobilinogen 4.0 in urine pregnancy should discuss their results with their healthcare provider to understand the implications and develop a plan for monitoring and management.
What Are the Symptoms Associated With Elevated Urobilinogen Levels?
Elevated urobilinogen levels during pregnancy may not always cause noticeable symptoms, but in some cases, they can lead to specific signs that warrant attention. Common symptoms associated with elevated urobilinogen include:
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes)
- Fatigue or weakness
- Abdominal pain or discomfort
- Dark urine or pale stools
If you experience any of these symptoms, it's important to consult your healthcare provider promptly for evaluation. Early detection and management can help prevent complications and ensure a healthy pregnancy journey.
How Can Urobilinogen Levels Be Managed During Pregnancy?
Managing urobilinogen levels during pregnancy involves a combination of lifestyle adjustments, dietary changes, and medical interventions, depending on the underlying cause. For women with urobilinogen 4.0 in urine pregnancy, a personalized approach is often necessary to address their specific needs and ensure optimal health for both mother and baby.
Lifestyle modifications, such as regular exercise, adequate hydration, and stress management, can support overall health and potentially influence urobilinogen levels. Dietary adjustments, including increased intake of liver-friendly foods like leafy greens, citrus fruits, and lean proteins, may also be beneficial. In some cases, healthcare providers may recommend supplements or medications to support liver function and address any underlying conditions.
Regular monitoring of urobilinogen levels is essential to track progress and make necessary adjustments to the care plan. Pregnant women should work closely with their healthcare providers to develop a comprehensive strategy that addresses their unique needs and promotes a healthy pregnancy.
Can Dietary Changes Help Lower Urobilinogen Levels?
Diet plays a crucial role in maintaining liver health and managing urobilinogen levels during pregnancy. For women with urobilinogen 4.0 in urine pregnancy, dietary adjustments can help support liver function and potentially reduce elevated levels. Incorporating liver-friendly foods into your diet can provide the nutrients and antioxidants needed to support healthy metabolic processes.
Here are some dietary tips to consider:
- Increase intake of fruits and vegetables, particularly those rich in antioxidants.
- Choose lean proteins, such as fish, chicken, and tofu, to support liver function.
- Limit processed foods and saturated fats, which can strain the liver.
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day.
While dietary changes alone may not be sufficient to address all causes of elevated urobilinogen, they can complement other interventions and promote overall health during pregnancy.
What Are the Best Foods for Liver Health During Pregnancy?
Supporting liver health during pregnancy is essential for managing urobilinogen levels and ensuring optimal health for both mother and baby. Some of the best foods for liver health include:
- Leafy greens, such as spinach and kale
- Citrus fruits, like oranges and lemons
- Lean proteins, including fish and chicken
- Whole grains, such as brown rice and quinoa
Incorporating these foods into your diet can provide the nutrients and antioxidants needed to support liver function and potentially reduce elevated urobilinogen levels.
What Are the Potential Risks of Elevated Urobilinogen Levels?
Elevated urobilinogen levels during pregnancy, such as urobilinogen 4.0 in urine pregnancy, can pose potential risks if left unaddressed. While some cases may be benign and related to normal physiological adaptations, others may indicate underlying health conditions that require medical attention. Understanding the potential risks associated with elevated urobilinogen is essential for ensuring a healthy pregnancy journey.
One of the primary concerns with elevated urobilinogen levels is the possibility of liver dysfunction or disease. This can affect the body's ability to process and excrete waste products, potentially leading to complications for both mother and baby. In severe cases, untreated liver issues can result in preterm labor, fetal distress, or other adverse outcomes. Pregnant women with elevated urobilinogen levels should work closely with their healthcare providers to monitor their health and address any underlying conditions.
Early detection and management of elevated urobilinogen levels can help mitigate these risks and promote a healthy pregnancy. Regular testing, lifestyle adjustments, and medical interventions, if necessary, can all play a role in managing this condition effectively.
How Can Pregnant Women Reduce the Risk of Liver Issues?
Pregnant women can take several steps to reduce the risk of liver issues and manage elevated urobilinogen levels effectively. These strategies include:
- Regular prenatal care and testing
- Healthy lifestyle choices, such as exercise and stress management
- Dietary adjustments to support liver function
- Timely medical interventions for underlying conditions
By adopting these practices, pregnant women can minimize the risk of complications and ensure a healthy pregnancy journey.
What Should Pregnant Women Do If They Have Elevated Urobilinogen Levels?
If you have elevated urobilinogen levels during