Imagine this: your beloved furry companion suddenly develops a mysterious illness that seems to defy explanation. It’s every pet owner’s worst nightmare, but the reality of "dog flesh eating bacteria" is more common than you might think. This alarming condition, scientifically referred to as necrotizing fasciitis in canines, has gained significant attention in recent years due to its rapid progression and potentially life-threatening consequences. While the term may sound alarming, understanding its causes, symptoms, and preventive measures can empower pet owners to take proactive steps in safeguarding their dogs’ health. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve deep into the world of flesh-eating bacteria in dogs, unraveling its complexities and providing practical advice for pet owners.
What makes "dog flesh eating bacteria" particularly concerning is its ability to spread rapidly, attacking soft tissues and causing severe damage in a matter of hours. This aggressive infection is caused by a group of bacteria, often including Streptococcus and Staphylococcus species, which invade the body through cuts, wounds, or even minor abrasions. Dogs with compromised immune systems or pre-existing health conditions are particularly vulnerable, making it crucial for pet owners to remain vigilant. By understanding the factors that contribute to this condition and recognizing its early warning signs, you can ensure your furry friend receives the care they need before the situation escalates.
As we navigate through this article, we’ll explore the science behind "dog flesh eating bacteria," its transmission pathways, and the steps you can take to protect your pet. From identifying the symptoms to understanding the treatment options available, this guide aims to equip you with the knowledge necessary to tackle this potentially devastating condition. Whether you’re a seasoned pet owner or a newcomer to the world of dogs, this article will provide valuable insights into maintaining your pet’s health and well-being. So, let’s dive in and uncover the truth about "dog flesh eating bacteria" and how you can keep your furry companion safe.
Read also:Why Does My Macbook Screen Have Lines A Comprehensive Guide To Diagnosing And Fixing Display Issues
Table of Contents
- What Causes Dog Flesh Eating Bacteria?
- How Does Dog Flesh Eating Bacteria Spread?
- Can Dog Flesh Eating Bacteria Affect Humans?
- Identifying Symptoms: What Should You Look For?
- How Is Dog Flesh Eating Bacteria Diagnosed?
- Treatment Options for Dog Flesh Eating Bacteria
- Preventive Measures: How Can You Protect Your Dog?
- FAQs About Dog Flesh Eating Bacteria
What Causes Dog Flesh Eating Bacteria?
At the heart of the "dog flesh eating bacteria" phenomenon lies a group of aggressive microorganisms capable of wreaking havoc on a dog’s body. These bacteria, primarily belonging to the Streptococcus and Staphylococcus families, thrive in environments where the immune system is weakened or compromised. While healthy dogs are less likely to contract this condition, those with pre-existing health issues, such as diabetes, cancer, or autoimmune disorders, are at higher risk. Additionally, factors like poor hygiene, unclean living conditions, and exposure to contaminated surfaces can contribute to the development of this infection.
One of the most common entry points for these bacteria is through open wounds, cuts, or scratches. Even minor abrasions can serve as gateways for these aggressive pathogens to invade the body. Once inside, they multiply rapidly, releasing toxins that destroy soft tissues and cause widespread inflammation. The bacteria’s ability to evade the immune system further complicates the situation, making it challenging for the body to combat the infection effectively. Understanding these underlying causes is the first step in preventing the onset of "dog flesh eating bacteria" and ensuring your pet remains healthy.
To mitigate the risk of infection, it’s essential to maintain proper hygiene practices and regularly inspect your dog’s skin for signs of injury or irritation. Keeping your pet’s living environment clean and free of contaminants can also play a significant role in reducing exposure to harmful bacteria. By addressing these potential risk factors, you can significantly lower the likelihood of your dog contracting this devastating condition.
How Does Dog Flesh Eating Bacteria Spread?
The transmission of "dog flesh eating bacteria" occurs through various pathways, making it a complex and multifaceted issue. Direct contact with infected animals or contaminated surfaces is one of the primary means of spread. For instance, if your dog comes into contact with another dog carrying the bacteria, there’s a possibility of transmission, especially if open wounds or cuts are present. Similarly, sharing items like toys, grooming tools, or bedding with an infected animal can increase the risk of exposure.
Environmental factors also play a significant role in the spread of this condition. Areas with poor sanitation, such as overcrowded kennels or unsanitary living conditions, can serve as breeding grounds for harmful bacteria. Additionally, natural disasters or extreme weather conditions can disrupt normal hygiene practices, further exacerbating the problem. Understanding these transmission pathways is crucial in implementing effective preventive measures and minimizing the risk of infection.
By maintaining proper hygiene practices, ensuring your pet’s living environment is clean and well-maintained, and avoiding contact with potentially infected animals, you can significantly reduce the chances of your dog contracting "dog flesh eating bacteria." Regular veterinary check-ups and vaccinations can also help strengthen your pet’s immune system, making it more resilient to infections.
Read also:Aaron Evans Love Island A Journey Through Reality Tv Fame
Can Dog Flesh Eating Bacteria Affect Humans?
One of the most pressing concerns for pet owners is whether "dog flesh eating bacteria" can pose a threat to human health. While the bacteria responsible for this condition primarily affect canines, there are instances where humans can contract similar infections through direct contact with infected animals. This cross-species transmission typically occurs when open wounds or cuts come into contact with contaminated surfaces or bodily fluids from an infected dog.
Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as the elderly, young children, or those with chronic health conditions, are particularly vulnerable to these infections. To minimize the risk of transmission, it’s crucial to practice good hygiene habits, such as washing hands thoroughly after handling pets and avoiding contact with open wounds. Additionally, seeking immediate medical attention if you suspect exposure to harmful bacteria can prevent the condition from escalating.
By understanding the potential risks associated with "dog flesh eating bacteria" and taking appropriate precautions, you can safeguard both your pet’s health and your own well-being. Regular communication with your veterinarian and healthcare provider can also provide valuable insights into preventive measures and treatment options.
Identifying Symptoms: What Should You Look For?
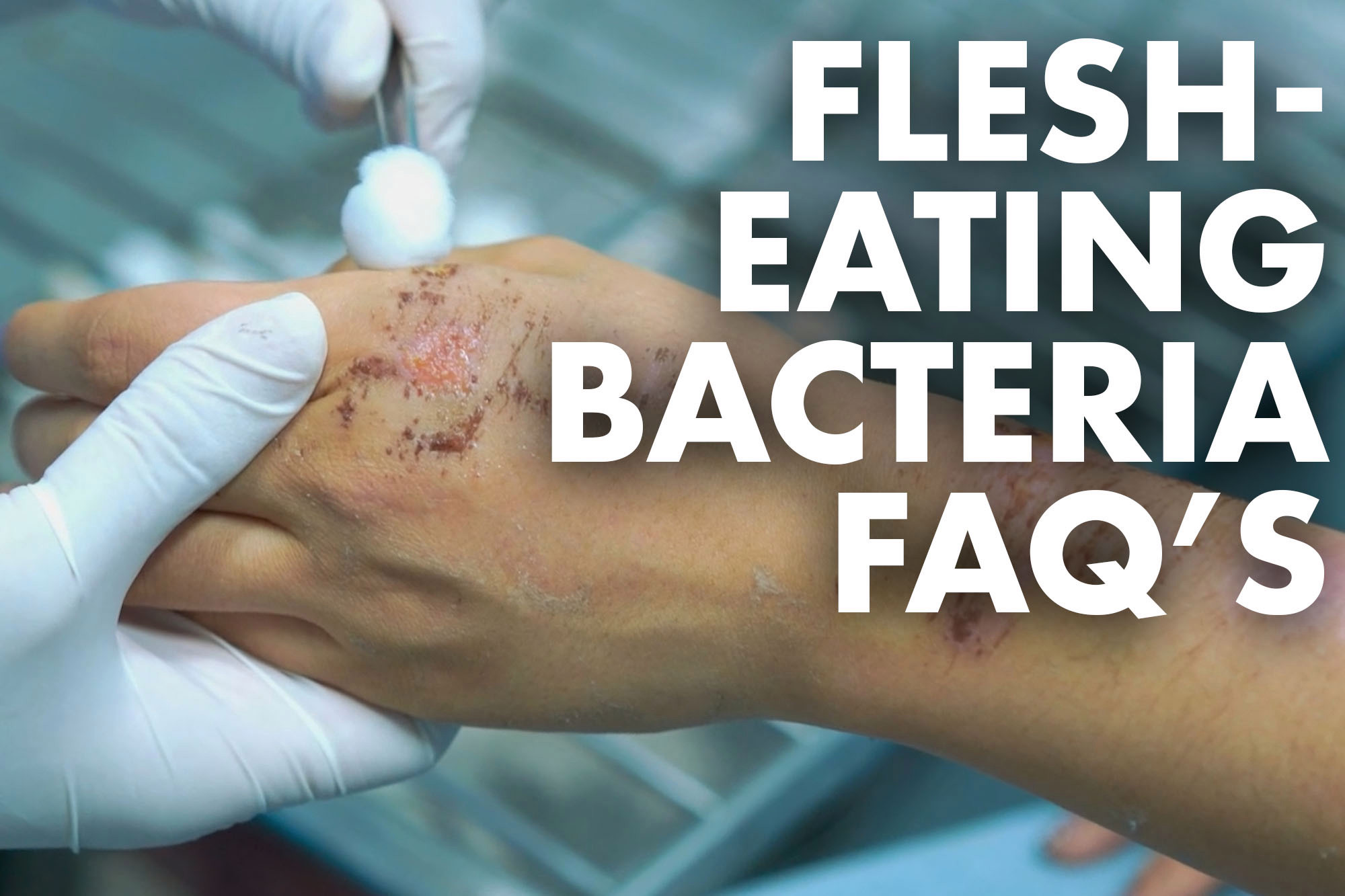
Recognizing the early warning signs of "dog flesh eating bacteria" is critical in ensuring timely intervention and treatment. One of the most noticeable symptoms is the presence of red, swollen, and painful areas on the skin, often accompanied by a foul odor. As the infection progresses, these areas may develop into ulcers or open sores, releasing pus or other discharge. In severe cases, the affected tissue may appear black or necrotic, indicating significant tissue damage.
Other symptoms to watch for include fever, lethargy, loss of appetite, and general discomfort. Dogs may also exhibit signs of distress, such as whimpering or reluctance to move, as the infection spreads and causes widespread inflammation. Early detection is key in preventing the condition from worsening, so it’s essential to monitor your pet closely for any unusual changes in behavior or appearance.
If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s crucial to seek veterinary care immediately. Delaying treatment can lead to severe complications, including sepsis or organ failure, which can be life-threatening. By familiarizing yourself with these warning signs and acting promptly, you can ensure your pet receives the care they need to recover fully.
How Is Dog Flesh Eating Bacteria Diagnosed?
Diagnosing "dog flesh eating bacteria" involves a combination of physical examination, laboratory tests, and imaging studies to determine the extent of the infection. Veterinarians typically begin by conducting a thorough physical examination, focusing on the affected areas and assessing the severity of the symptoms. Blood tests, urine analysis, and tissue samples may also be collected to identify the specific bacteria responsible for the infection and determine the most effective treatment options.
In some cases, imaging techniques such as X-rays or ultrasounds may be used to evaluate the extent of tissue damage and monitor the progression of the infection. These diagnostic tools provide valuable insights into the underlying condition and help guide treatment decisions. Early and accurate diagnosis is essential in ensuring successful outcomes and minimizing the risk of complications.
Once a diagnosis is confirmed, your veterinarian will work closely with you to develop a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to your pet’s specific needs. Regular follow-up appointments and monitoring are crucial in assessing the effectiveness of the treatment and making necessary adjustments.
Treatment Options for Dog Flesh Eating Bacteria
Treating "dog flesh eating bacteria" requires a multifaceted approach, combining antibiotic therapy, surgical intervention, and supportive care to address the infection’s underlying causes and promote healing. Antibiotics are often the first line of defense, targeting the specific bacteria responsible for the infection and preventing further spread. In severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to remove damaged or necrotic tissue, reducing the bacterial load and allowing healthy tissue to regenerate.
Supportive care plays a vital role in the recovery process, focusing on managing symptoms, enhancing the immune system, and promoting overall well-being. This may include fluid therapy to combat dehydration, pain management to alleviate discomfort, and nutritional support to ensure your pet receives the necessary nutrients for healing. Regular monitoring and follow-up appointments are essential in tracking progress and adjusting treatment as needed.
Collaborating closely with your veterinarian and adhering to the prescribed treatment plan is crucial in ensuring a successful outcome. By addressing the infection promptly and effectively, you can help your pet overcome this challenging condition and regain their health and vitality.
Preventive Measures: How Can You Protect Your Dog?
Preventing "dog flesh eating bacteria" involves adopting proactive measures to minimize the risk of infection and maintain your pet’s overall health. Regular veterinary check-ups and vaccinations are essential in strengthening your dog’s immune system and reducing susceptibility to infections. Maintaining proper hygiene practices, such as regular grooming and cleaning of living areas, can also play a significant role in preventing the spread of harmful bacteria.
Additionally, monitoring your pet for signs of injury or irritation and addressing these issues promptly can help prevent the onset of infections. Providing a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients and ensuring your dog receives adequate exercise and mental stimulation can further enhance their immune system and overall well-being. By taking these preventive measures, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of your dog contracting "dog flesh eating bacteria" and ensure they lead a healthy, happy life.
Remember, early detection and intervention are key in managing this condition effectively. By staying informed and vigilant, you can protect your furry companion from the potentially devastating effects of "dog flesh eating bacteria" and enjoy a lifetime of joy and companionship together.
FAQs About Dog Flesh Eating Bacteria
Here are some frequently asked questions and their answers to help you better understand "dog flesh eating bacteria" and its implications for your pet’s health.
1. Can "dog flesh eating bacteria" be cured completely?
Yes, with prompt and appropriate treatment, "dog flesh eating bacteria" can be cured completely. Early intervention, including antibiotic therapy and surgical intervention if necessary, is crucial in ensuring successful outcomes. Regular follow-up appointments and adherence to the prescribed treatment plan are essential in monitoring progress and preventing recurrence.
2. Are certain breeds more prone to "dog flesh eating bacteria"?
While any dog can contract "dog flesh eating bacteria," certain breeds with predisposed health conditions or weakened immune systems may be more susceptible. Additionally, dogs living in unsanitary conditions or exposed to contaminated environments are at higher risk. Maintaining proper hygiene and regular veterinary care can help mitigate these risks and ensure your pet remains healthy.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the complexities of "dog flesh eating bacteria" is essential in safeguarding your pet’s health and well-being. By recognizing its causes, symptoms, and preventive measures, you can take proactive steps in protecting your furry companion from this potentially devastating condition. Remember, early detection and intervention are key in ensuring successful outcomes, so it’s crucial to remain vigilant and seek veterinary care promptly if you suspect any signs of infection. With proper care and attention, you can help your pet overcome this challenge and enjoy a lifetime of happiness and companionship together.
Meta Description: Uncover the truth about dog flesh eating bacteria and learn how to protect your furry friend. This comprehensive guide covers causes, symptoms, treatment, and prevention tips for pet owners.