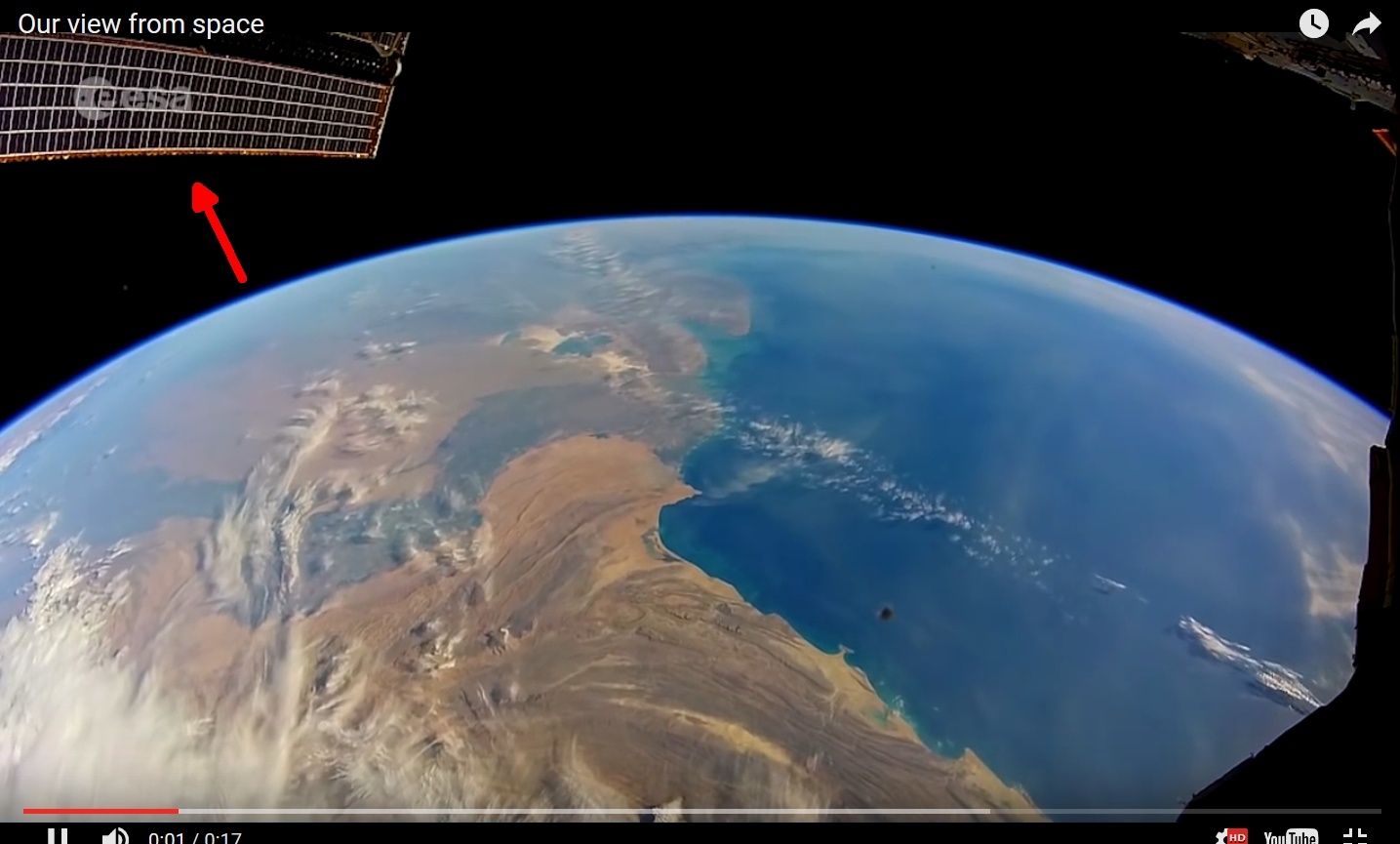
Have you ever wondered what Earth really looks like from the vastness of space? For centuries, humanity has been fascinated by our planet's appearance and the intricate details that make it unique. With advancements in satellite technology and space exploration, we now have a clearer understanding of Earth's true form. From its swirling oceans to its towering mountain ranges, our planet is a breathtaking masterpiece of nature. This article delves deep into the mysteries of Earth's appearance, uncovering its beauty and complexity through the eyes of astronauts, scientists, and modern technology.
Earth, often referred to as the "Blue Planet," stands out in our solar system as a vibrant and dynamic world. Unlike the barren landscapes of Mars or the gas giants like Jupiter, Earth is teeming with life, color, and diversity. From the lush green forests of the Amazon to the icy expanses of Antarctica, every corner of our planet tells a story of resilience and adaptability. But what does Earth look like from space? How do astronauts describe the view, and what insights do satellites provide about our planet's surface? These questions have intrigued scientists and space enthusiasts alike, sparking a deeper appreciation for the world we call home.
As we explore the topic of "what Earth really looks like," we'll journey through its layers, landscapes, and atmospheric wonders. This article will take you on a fascinating voyage, uncovering the mysteries of Earth's appearance, its environmental changes, and the technologies that allow us to see it in unprecedented detail. Whether you're a space enthusiast, a nature lover, or simply curious about our planet, this exploration promises to reveal the awe-inspiring beauty of Earth as never seen before.
Read also:Why Does My Macbook Screen Have Lines A Comprehensive Guide To Diagnosing And Fixing Display Issues
Table of Contents
- What Earth Really Looks Like from Space
- How Does Satellite Technology Help Us Understand Earth?
- Why Is Earth Called the Blue Planet?
- What Are the Major Landforms on Earth?
- How Does Earth's Atmosphere Affect Its Appearance?
- What Are the Effects of Climate Change on Earth's Appearance?
- How Do Astronauts Describe Earth's Beauty?
- What Future Technologies Will Reveal About Earth's Looks?
- FAQs
- Conclusion
What Earth Really Looks Like from Space
When astronauts aboard the International Space Station (ISS) look down at our planet, they are greeted by a mesmerizing sight. Earth appears as a vibrant blue sphere, dotted with swirling white clouds, vast green continents, and sprawling brown mountain ranges. This breathtaking view is often described as the " Overview Effect," a term coined to describe the profound shift in perspective that astronauts experience when they witness the planet's fragility and interconnectedness from space.
The "Blue Planet" nickname stems from the dominant presence of water covering approximately 71% of Earth's surface. The oceans, which appear deep blue from space, are the largest continuous feature of our planet. Surrounding these vast bodies of water are the landmasses, which range in color from lush green to arid brown, depending on the region. Deserts, forests, and urban areas create a tapestry of hues that add to the planet's visual complexity.
Astronauts often remark on the thin layer of atmosphere that surrounds Earth, resembling a fragile blue haze. This layer, which protects life on the surface, is a mere fraction of the planet's diameter but plays a crucial role in maintaining the conditions necessary for life. From space, this delicate balance becomes all the more apparent, reinforcing the importance of preserving our environment.
How Does Satellite Technology Help Us Understand Earth?
Satellite technology has revolutionized our understanding of "what Earth really looks like." Modern satellites equipped with advanced sensors and cameras provide high-resolution images of the planet's surface, capturing everything from weather patterns to geological formations. These images allow scientists to monitor changes in Earth's landscape, track natural disasters, and study the effects of human activity on the environment.
One of the most significant contributions of satellite technology is its ability to provide real-time data. For instance, weather satellites continuously monitor atmospheric conditions, enabling meteorologists to predict storms, hurricanes, and other weather phenomena with greater accuracy. Similarly, Earth observation satellites help track deforestation, melting ice caps, and rising sea levels, offering valuable insights into the impacts of climate change.
Beyond scientific research, satellite imagery has practical applications in fields such as agriculture, urban planning, and disaster management. Farmers use satellite data to optimize crop yields, while city planners rely on it to design sustainable infrastructure. In times of crisis, satellite imagery plays a critical role in disaster response efforts, providing emergency responders with up-to-date information about affected areas.
Read also:Exploring The World Of Ed Edd N Eddy Sisters A Comprehensive Guide
Why Is Earth Called the Blue Planet?
The nickname "Blue Planet" highlights the dominant presence of water on Earth's surface. Oceans, seas, and lakes cover more than two-thirds of the planet, giving it a predominantly blue appearance from space. This vast expanse of water is not only visually striking but also essential for sustaining life. The oceans regulate Earth's climate, provide food and resources, and support a diverse array of marine ecosystems.
While water is the primary reason for Earth's blue hue, other factors contribute to its appearance. The atmosphere scatters sunlight in such a way that blue wavelengths are more visible, enhancing the planet's overall color. This phenomenon, known as Rayleigh scattering, creates the illusion of a deeper blue than what is actually present. Additionally, the reflection of sunlight on the ocean surface adds to the planet's radiant glow.
The term "Blue Planet" also serves as a reminder of Earth's uniqueness in the solar system. No other planet in our neighborhood has liquid water on its surface, making Earth a rare and precious gem in the cosmic landscape. This distinction underscores the importance of protecting our planet's resources and preserving its natural beauty for future generations.
What Are the Major Landforms on Earth?
Earth's diverse landscapes are shaped by a variety of geological processes, resulting in a wide range of landforms. From towering mountains to expansive plains, these features contribute to the planet's visual complexity and ecological diversity. Understanding the major landforms on Earth provides valuable insights into the forces that shape our world and the ecosystems they support.
Mountains are among the most prominent landforms, formed by tectonic activity, volcanic eruptions, or erosion. The Himalayas, Andes, and Rockies are just a few examples of mountain ranges that dominate the planet's surface. These towering structures not only influence weather patterns but also serve as vital water sources for millions of people. Rivers originating from mountain regions carry nutrients and sediments to lower elevations, enriching the soil and supporting agriculture.
Plains, on the other hand, are vast, flat areas that cover large portions of Earth's surface. These regions are often fertile and well-suited for farming, making them crucial for food production. Examples include the Great Plains of North America, the Pampas of South America, and the steppes of Eurasia. Deserts, another significant landform, occupy arid regions with little rainfall. Despite their harsh conditions, deserts are home to unique plant and animal species adapted to survive in extreme environments.
How Does Earth's Atmosphere Affect Its Appearance?
Earth's atmosphere plays a pivotal role in shaping the planet's appearance from space. This thin layer of gases not only protects life on the surface but also influences how Earth looks to observers above. The atmosphere scatters sunlight, creating the blue hue that dominates the planet's color palette. Without this scattering effect, Earth would appear much darker and less vibrant.
In addition to scattering light, the atmosphere also refracts it, bending the path of sunlight as it passes through different layers. This refraction can cause the planet to appear slightly larger than it actually is, creating an optical illusion known as atmospheric lensing. During sunrise and sunset, the atmosphere further enhances Earth's beauty by casting a golden glow over its surface, a phenomenon often described as the "golden hour."
The presence of clouds adds another layer of complexity to Earth's appearance. These fluffy white formations reflect sunlight, creating bright patches against the blue backdrop. Cloud patterns vary depending on weather conditions, providing valuable information about atmospheric dynamics. By studying cloud formations, scientists can gain insights into climate patterns, weather systems, and the overall health of the planet's atmosphere.
What Are the Effects of Climate Change on Earth's Appearance?
Climate change is leaving an indelible mark on Earth's appearance, altering its landscapes and ecosystems in profound ways. Rising temperatures, melting ice caps, and shifting weather patterns are just a few examples of the changes occurring across the planet. These transformations not only affect the natural world but also have far-reaching implications for human societies.
One of the most visible impacts of climate change is the shrinking of polar ice caps. As global temperatures rise, glaciers and ice sheets are melting at an alarming rate, causing sea levels to rise and threatening coastal communities. The loss of ice also affects Earth's albedo, or reflectivity, reducing the amount of sunlight reflected back into space and exacerbating global warming. From space, this change is evident in the diminishing white patches at the planet's poles.
Deforestation, another consequence of climate change, is transforming Earth's landscapes by reducing the amount of green cover. Forests play a critical role in regulating the climate by absorbing carbon dioxide and producing oxygen. Their destruction not only contributes to global warming but also disrupts local ecosystems, leading to biodiversity loss and soil degradation. Satellite imagery clearly shows the expansion of barren areas where once-thriving forests stood.
How Do Astronauts Describe Earth's Beauty?
Astronauts who have had the privilege of viewing Earth from space often describe it as a work of art. The planet's beauty, they say, is both humbling and inspiring, evoking a deep sense of connection to the world below. Many astronauts report experiencing the "Overview Effect," a profound shift in perspective that arises from witnessing Earth's fragility and interconnectedness firsthand.
One common observation among astronauts is the striking contrast between Earth's vibrant colors and the blackness of space. The blue of the oceans, the green of the forests, and the white of the clouds stand out against the dark void, creating a visual masterpiece that defies description. Some astronauts compare the experience to looking at a living, breathing organism, pulsing with energy and life.
Others emphasize the importance of Earth's atmosphere, which appears as a thin blue haze surrounding the planet. This delicate layer, they note, is what makes life possible, protecting us from the harsh conditions of space. The realization of Earth's vulnerability and the need to protect it often becomes a driving force for astronauts upon their return to Earth.
What Future Technologies Will Reveal About Earth's Looks?
As technology continues to advance, new tools and techniques will provide even greater insights into "what Earth really looks like." Innovations in satellite imaging, remote sensing, and artificial intelligence are paving the way for more detailed and accurate observations of the planet's surface and atmosphere. These advancements promise to enhance our understanding of Earth's complex systems and the challenges it faces.
One promising development is the use of hyperspectral imaging, which captures data across multiple wavelengths of light. This technology allows scientists to detect subtle variations in Earth's surface composition, revealing details that are invisible to the naked eye. Hyperspectral imaging has applications in agriculture, mineral exploration, and environmental monitoring, offering new ways to manage resources and mitigate the impacts of climate change.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is another game-changer in the field of Earth observation. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data collected by satellites and sensors, identifying patterns and trends that might otherwise go unnoticed. This capability enables scientists to make more informed decisions about resource management, disaster response, and climate adaptation.
FAQs
What Causes Earth's Blue Color?
Earth's blue color is primarily due to the presence of water, which covers approximately 71% of its surface. The scattering of sunlight by the atmosphere also enhances this blue hue, creating the illusion of a deeper blue than what is actually present.
How Does Climate Change Affect Earth's Appearance?
Climate change is altering Earth's appearance in several ways, including the melting of polar ice caps, deforestation, and changes in cloud patterns. These transformations not only impact the natural world but also have far-reaching implications for human societies.
Why Is Protecting Earth's Atmosphere Important?
Earth's atmosphere is crucial for protecting life on the surface by regulating temperature, filtering harmful radiation, and maintaining the conditions necessary for survival. Its frag